Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, stiffness, and swelling. Unlike osteoarthritis, which typically develops due to wear and tear on the joints, RA is characterized by the immune system attacking healthy tissues, leading to joint damage and other complications if left untreated.
Understanding the Importance of Early Detection
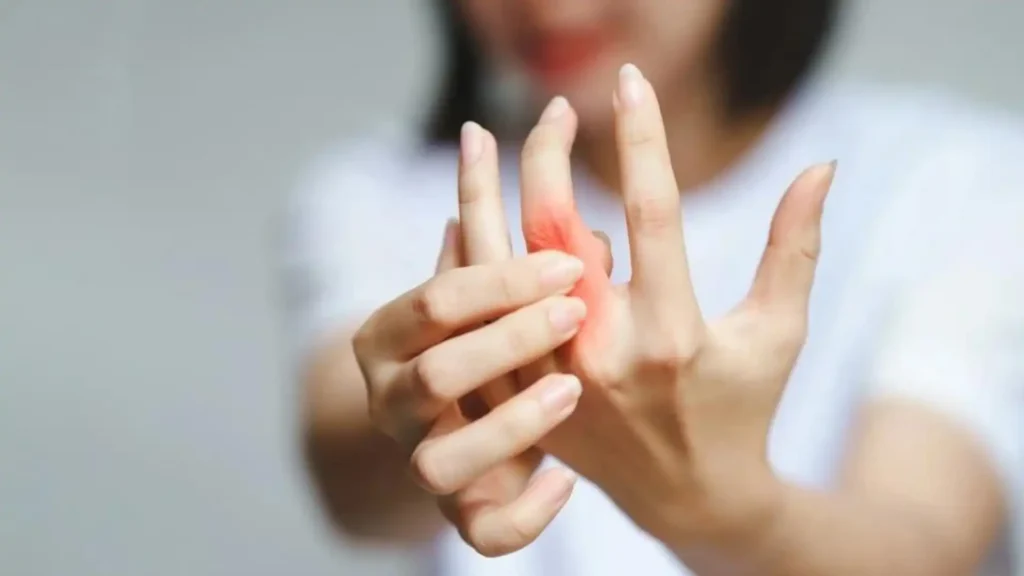
Early detection of RA is crucial for effective management and prevention of irreversible joint damage. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms can lead to prompt diagnosis and intervention, ultimately improving long-term outcomes and quality of life for individuals with RA.
Common Early Signs and Symptoms
1. Joint Pain and Stiffness
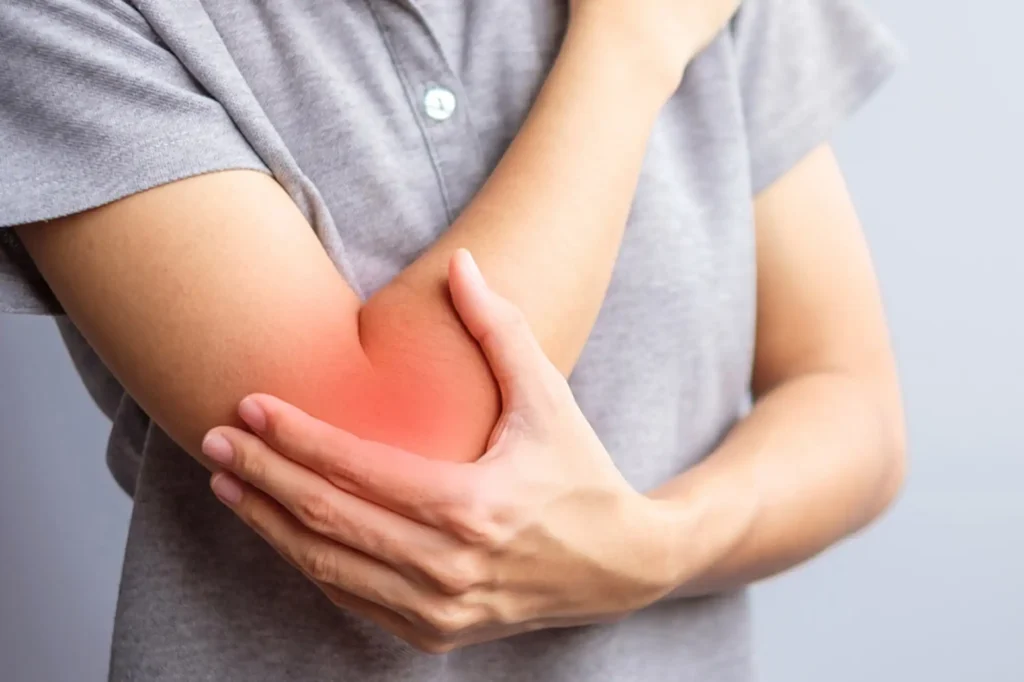
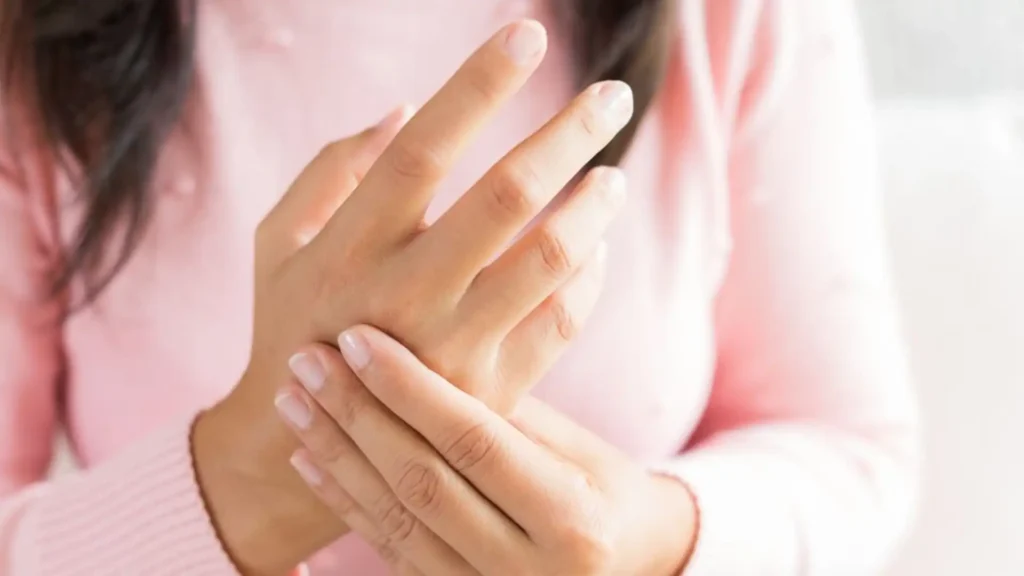
One of the earliest symptoms of RA is persistent joint pain, often accompanied by stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity. This pain and stiffness may initially affect small joints such as those in the fingers, hands, wrists, and toes, gradually progressing to larger joints like the knees, ankles, and shoulders.
2. Fatigue
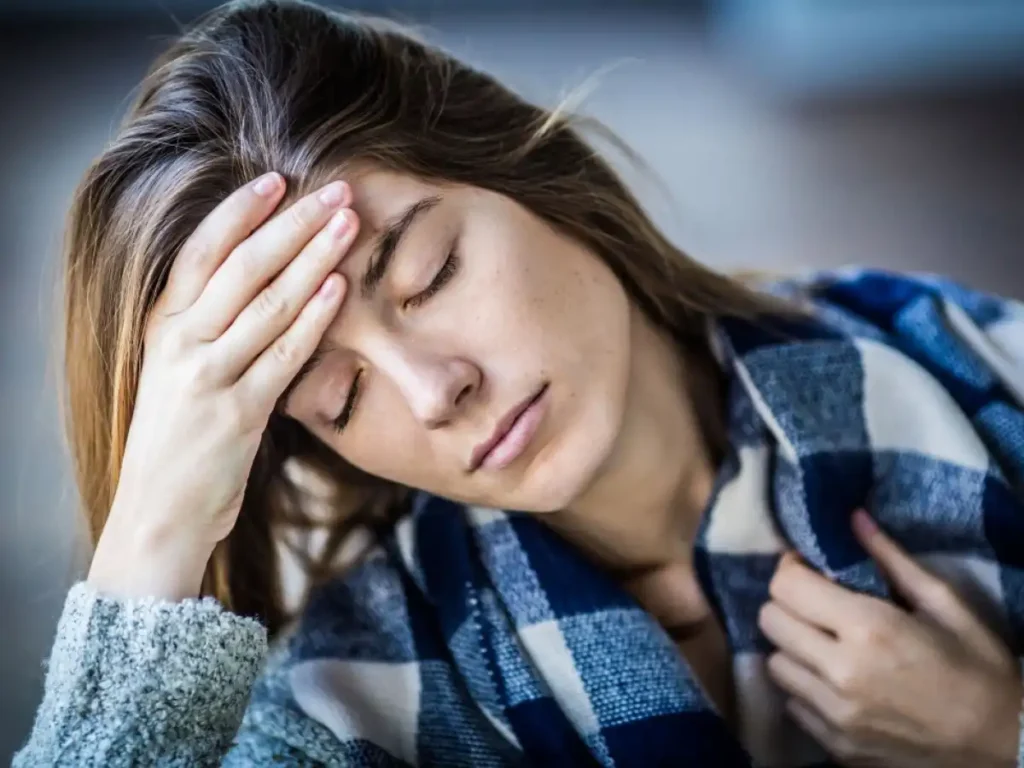

Unexplained fatigue or exhaustion, even after adequate rest, is another common early sign of RA. This overwhelming fatigue can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life, often exacerbating other symptoms associated with the condition.
3. Joint Swelling and Tenderness
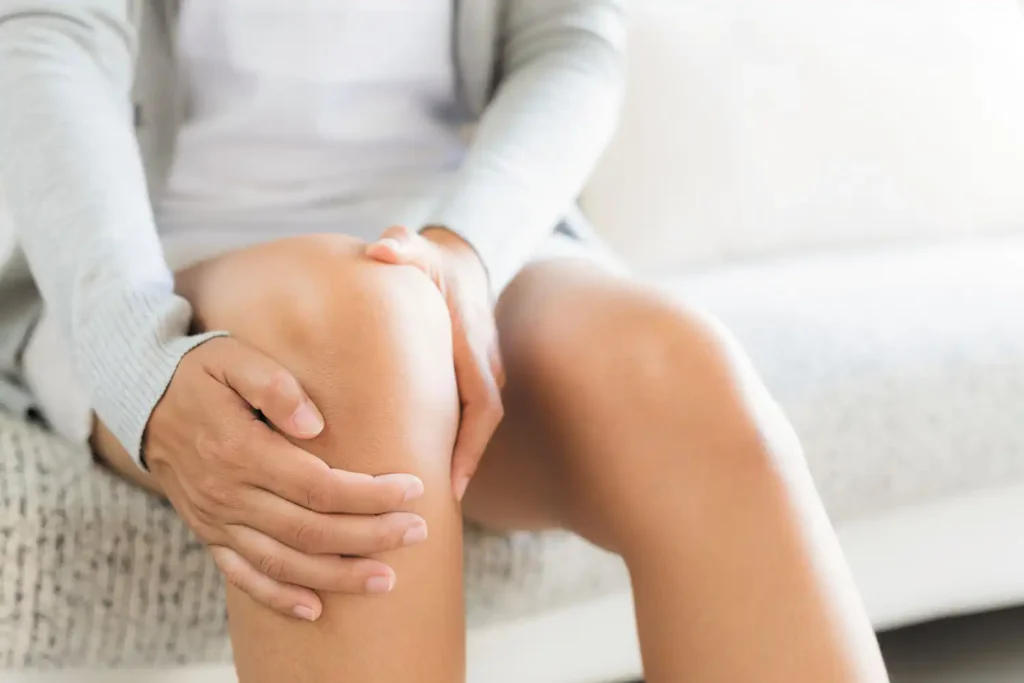

Inflammation of the synovium, the lining of the joints, leads to swelling and tenderness in affected areas. Visible swelling and a feeling of warmth around the joints may be early indicators of RA and should prompt further evaluation by a healthcare professional.
4. Morning Stiffness
Morning stiffness lasting for more than an hour, particularly in the joints, is a hallmark symptom of RA. This stiffness can be severe and may gradually improve with movement throughout the day but tends to recur after periods of rest or inactivity.
5. Reduced Range of Motion
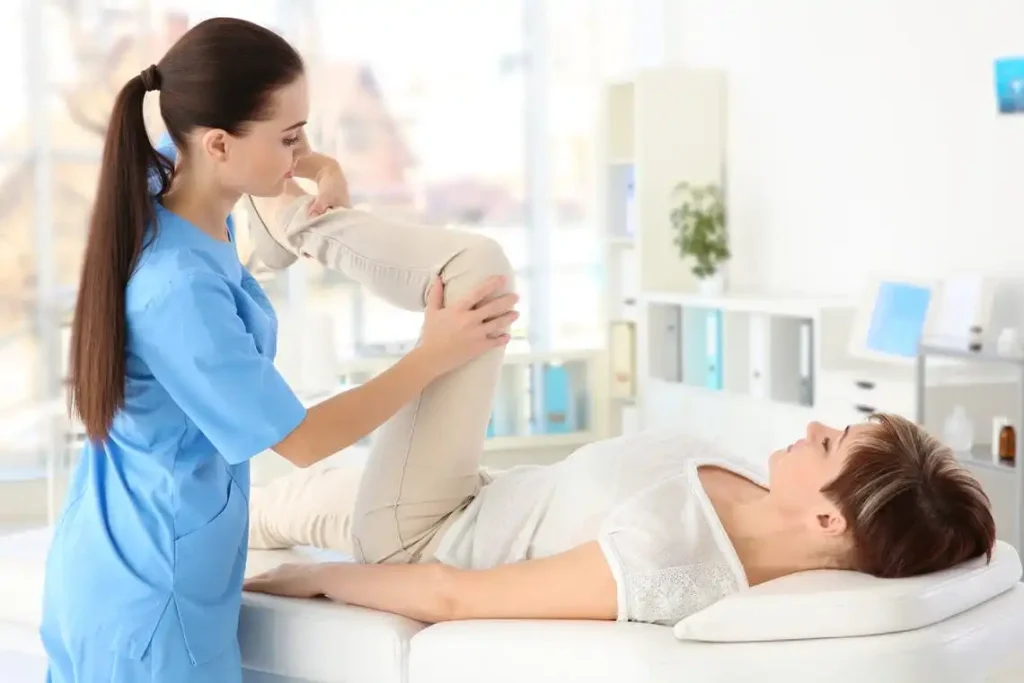

As RA progresses, individuals may experience a decreased range of motion in the affected joints. This limitation can interfere with daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs, and performing routine tasks, significantly impacting overall mobility and function.
6. Systemic Symptoms
In addition to joint-related symptoms, RA can also manifest with systemic symptoms such as fever, weight loss, and a general feeling of malaise. These nonspecific symptoms may accompany joint symptoms or present independently, highlighting the systemic nature of the disease.
Risk Factors and Diagnosis
Several factors increase the risk of developing RA, including genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and certain lifestyle factors. While there is no single diagnostic test for RA, healthcare providers typically rely on a combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging studies, and laboratory tests to confirm the diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
Early recognition of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis is paramount for timely diagnosis and intervention. By staying vigilant and seeking medical evaluation if experiencing any of the aforementioned symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing their condition and improving their overall quality of life.
By providing comprehensive information on the early signs and symptoms of RA, we aim to empower individuals to recognize potential warning signs and take proactive steps towards early detection and management, ultimately improving outcomes and quality of life for those affected by this chronic autoimmune condition.
Discover more trends:
- Keep an Eye Out for Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Guide
- Nicole Kidman’s Revealing Dress Sparks a Heated Discussion
- Watch Out For The Early Signs Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Follow us on Facebook





