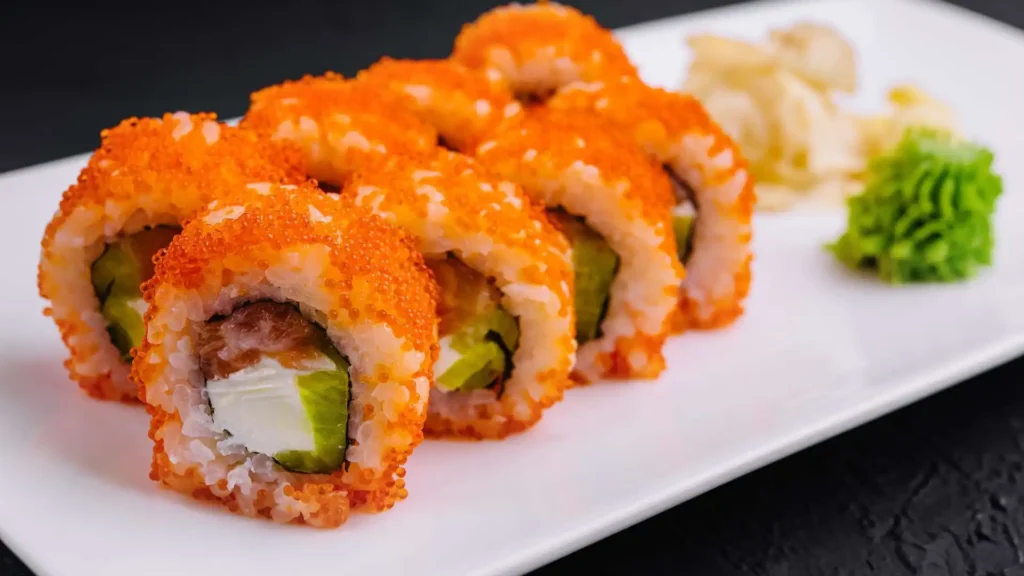
Masago, also known as smelt roe, is an intriguing ingredient widely used in Asian cuisine, especially in sushi. These tiny, flavorful fish eggs come from the capelin fish, a small species found in the cold waters of the North Atlantic, North Pacific, and Arctic Oceans. Aside from its unique taste and texture, masago is also celebrated for its impressive nutritional profile, making it a healthy addition to various dishes. This article will delve into the nutritional benefits, potential downsides, culinary uses, and ecological concerns surrounding masago, ensuring you have a well-rounded understanding of this fascinating delicacy.
Nutritional Profile of Masago
Masago is a powerhouse of essential nutrients packed into tiny, vibrant eggs. Here’s a detailed look at its nutritional content per ounce (28 grams):
- Calories: 40
- Fat: 2 grams
- Protein: 6 grams
- Carbohydrates: less than 1 gram
- Vitamin C: 7% of the Daily Value (DV)
- Vitamin E: 10% of the DV
- Riboflavin (B2): 12% of the DV
- Vitamin B12: 47% of the DV
- Folate (B9): 6% of the DV
- Phosphorus: 11% of the DV
- Selenium: 16% of the DV
Health Benefits of Masago
- Rich Source of Protein
- Despite their small size, masago eggs pack a punch when it comes to protein. A single ounce delivers 6 grams of high-quality protein, comparable to the amount found in one large egg. This makes masago an excellent choice for those looking to increase their protein intake.
- Protein is crucial for muscle repair, enzyme function, and overall body maintenance. The protein in masago contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete protein source.
- High in Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that play a vital role in heart health, reducing inflammation, and supporting brain function. Masago is a rich source of these beneficial fats, which are particularly important because the body cannot produce them on its own.
- Regular consumption of omega-3 rich foods like masago has been linked to a lower risk of heart disease, improved cognitive function, and reduced inflammation throughout the body.
- Low in Mercury
- One of the significant advantages of masago is its low mercury content. Since capelin fish are small and low on the food chain, they accumulate less mercury compared to larger predatory fish like mackerel and swordfish. This makes masago a safer choice for regular consumption, especially for those concerned about mercury exposure.
- Abundant in Selenium and Vitamin B12
- Selenium is a potent antioxidant that helps reduce oxidative stress, supports thyroid function, and boosts the immune system. Masago is a good source of this essential mineral, providing 16% of the DV per ounce.
- Vitamin B12 is critical for nerve health, DNA synthesis, and energy production. Masago offers a significant amount of this vital vitamin, ensuring you meet nearly half of your daily requirements with just one ounce.
Potential Downsides of Masago
- Ecological Concerns
- While masago is nutritious, its production raises several ecological concerns. The fishing methods used for capelin can inadvertently capture other marine species, including endangered ones. Environmental organizations have expressed worries about the sustainability of capelin fishing and its impact on marine ecosystems.
- The demand for masago often targets egg-bearing female capelin, which can negatively affect the species’ population over time. Sustainable fishing practices and mindful consumption are essential to mitigate these ecological impacts.
- High Sodium Content
- Like many other fish roe products, masago is high in sodium. It is often mixed with salty ingredients such as soy sauce and additional salt to enhance its flavor, which can significantly increase its sodium content. High sodium intake can lead to elevated blood pressure and other health issues, particularly in salt-sensitive individuals.
- Risk of Allergic Reaction
- Individuals with seafood allergies should avoid masago, as it can trigger allergic reactions. Fish roe contains vitellogenin, a fish egg yolk protein identified as a potential allergen. Even those without known seafood allergies may experience allergic reactions, including rashes, narrowing of the airways, and low blood pressure.
- Presence of Additives
- Masago can contain additives like high fructose corn syrup and monosodium glutamate (MSG), which some people may want or need to avoid. Regular consumption of high fructose corn syrup is linked to disrupted metabolism and insulin resistance, while MSG, though generally safe, can cause adverse reactions in some individuals.
Uses of Masago in Cuisine
Masago’s semi-crunchy texture and salty flavor make it a versatile ingredient in various dishes. Here are some creative ways to incorporate masago into your culinary repertoire:
- Sushi Rolls: Top homemade sushi rolls with a few teaspoons of masago for added flavor and visual appeal. Its bright color and distinctive texture can elevate the presentation and taste of your sushi.
- Appetizers: Combine masago with cheese and fruit to create a unique and flavorful appetizer. The contrast between the creamy cheese, sweet fruit, and salty masago makes for an exciting taste experience.
- Rice and Noodle Dishes: Add masago to rice dishes or Asian noodle recipes for a burst of flavor and texture. It pairs well with a variety of ingredients, enhancing the overall dish.
- Poke Bowls: Use masago as a topping for poke bowls, adding a touch of color and a delightful crunch to the mix of fresh fish, vegetables, and rice.
- Dips: Mix masago into wasabi or spicy mayonnaise to create a flavorful dip for sushi rolls, vegetables, or seafood.
Conclusion
Masago is a unique and nutritious ingredient that can enhance a wide variety of dishes. Its high protein content, beneficial omega-3 fatty acids, and essential vitamins make it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. However, it is important to consume in moderation due to its high sodium content and potential ecological concerns. For those who enjoy seafood, offers a delightful way to boost the nutritional value and flavor of their meals.
Masago is a nutrient-dense food that provides a unique taste and texture to various dishes. Its high protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential vitamins make it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. However, it should be consumed in moderation due to its sodium content and ecological concerns. When used mindfully, can be a delightful ingredient that enhances both the flavor and nutritional profile of your meals.
Discover more trends:
- Jeera is Cumin: Effective Home Remedies for Digestion, Skin, and Overall Health
- 11 Foods To Get Rid Of Knee Pain Naturally
- How Medicinal Mushrooms Boost Your Brain Health
- 10 Foods to Avoid If You Have Arthritis
- 8 Activities to Avoid on an Empty Stomach
- Follow us on Facebook
- Follow us on Pinterest