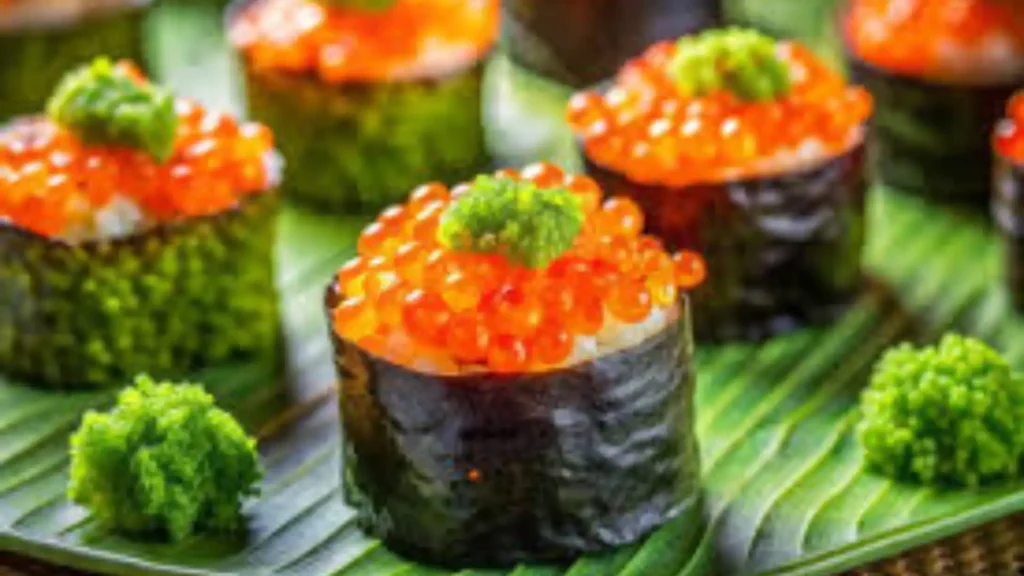
If you’re a fan of sushi, chances are you’ve encountered tiny, crunchy orange fish eggs that add a burst of flavor to your meal. But what exactly are they, and are they good for you? For the uninitiated, these fish eggs are known as roe from the capelin fish, a species found in cold-water regions. Masago, This delicacy has become a popular topping for various dishes, especially sushi, because of its bright color, unique texture, and salty flavor. However, as with any food, there are both benefits and potential downsides to eating roe.
In this article, we’ll explore what capelin roe is, the benefits it offers, and some of the downsides to consider if you’re thinking about incorporating more of it into your diet. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of capelin fish eggs!
What Is Capelin Roe? Masago
Capelin roe is the tiny eggs harvested from the capelin fish, a species closely related to smelt. These fish are typically found in the cold waters of the Atlantic and Arctic oceans. The roe is prized for its small, crunchy texture and mild flavor, making it an excellent complement to various dishes, particularly in Japanese cuisine.
What Does It Look Like?
Capelin roe is often mistaken for tobiko, another type of fish roe, but the two have subtle differences. Capelin roe is much smaller in size and tends to have a softer texture compared to tobiko, which is larger and crunchier. Typically, capelin roe is naturally pale yellow in color, but it’s often dyed bright orange to make it more visually appealing when used in dishes like sushi rolls.
How Is It Harvested?
Capelin fish spawn in large numbers, making the process of harvesting their eggs relatively easy. Fishermen catch the fish, then extract the roe, which is processed and often dyed before being sold to markets and restaurants. You’ll commonly see it used as a topping for sushi, sashimi, or other seafood dishes.
What Does It Taste Like?
Capelin roe has a salty, slightly bitter flavor, and its texture is crunchy yet soft. It pairs well with ingredients like soy sauce, wasabi, and nori, offering a delightful contrast in sushi and other dishes. While it’s typically used as a garnish, it’s flavorful enough to enhance the overall taste of a meal without overpowering other ingredients.
Benefits of Capelin Roe
Despite its small size, capelin roe packs quite the nutritional punch. It’s rich in essential nutrients and offers several health benefits, making it a popular choice for those looking to add a bit of extra nutrition to their diet.
High in Protein and Omega-3 Fatty Acids
One of the primary benefits of capelin roe is its high protein content. A small serving provides a good amount of protein, crucial for muscle growth and repair. Additionally, it’s packed with omega-3 fatty acids, known for their heart-health benefits. Omega-3s help reduce inflammation, lower blood pressure, and improve heart function.
Key Nutritional Benefits:
- High in protein: Great for muscle repair and building.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Supports heart health and reduces inflammation.
- Rich in B-vitamins: Vital for energy metabolism and brain function.
- Good source of selenium: An antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage.
Supports Eye and Brain Health
The omega-3 fatty acids in capelin roe aren’t just good for your heart; they also support brain and eye health. Omega-3s play a significant role in reducing the risk of cognitive decline and age-related macular degeneration. They can help maintain overall cognitive function, improve focus, and even boost your mood.
Low in Calories and Fat
Compared to many other protein-rich foods, capelin roe is relatively low in calories and fat. This makes it a great option for those watching their calorie intake or looking for lighter alternatives to heavier, fattier foods. A small portion of roe is enough to add flavor and texture to a meal without significantly impacting your daily caloric intake.
Downsides of Capelin Roe
While capelin roe offers numerous health benefits, it’s not without its downsides. Like many other types of fish eggs, it comes with a few potential drawbacks that are important to keep in mind if you’re planning on incorporating it into your diet.
High Sodium Content
One of the main concerns with capelin roe is its sodium content. A small serving contains a significant amount of sodium, which can contribute to high blood pressure and other cardiovascular issues if consumed in excess. If you’re someone who needs to monitor your sodium intake, it’s essential to enjoy roe in moderation. Masago.
Risk of Allergies
Fish roe can trigger allergic reactions in some individuals, particularly those with a sensitivity to seafood or fish proteins. Common symptoms of a fish egg allergy include itching, swelling, hives, and, in severe cases, difficulty breathing. If you have a history of seafood allergies, it’s best to avoid capelin roe or consult your healthcare provider before trying it.
Potential for Contaminants
As with any seafood product, there’s always the potential for contaminants like mercury and other heavy metals. Capelin, the fish from which roe is sourced, is relatively low on the food chain, meaning it’s less likely to contain high levels of mercury. However, it’s still important to be mindful of where your roe is sourced, especially if you consume seafood regularly.
Downsides at a Glance:
- High sodium content: Can contribute to high blood pressure.
- Potential allergens: May trigger allergic reactions in some individuals.
- Possible contaminants: Risk of mercury or other pollutants.
Is It Sustainable?
Sustainability is an essential consideration when it comes to seafood, and fortunately, capelin is generally considered to be a sustainable fish species. The populations are well-managed, and the fish is caught using methods that minimize bycatch. However, it’s always a good idea to check for sustainability certifications or ask your supplier about the sourcing practices to ensure you’re making eco-conscious choices. Masago.
Environmental Impact, Masago
While the capelin fishery is relatively sustainable, the environmental impact of overfishing and ocean pollution can affect populations. Supporting fisheries that follow sustainable practices ensures that we can continue enjoying roe for years to come.
How to Enjoy Capelin Roe
Capelin roe is incredibly versatile and can be used in a variety of dishes, especially if you’re a fan of Japanese cuisine. Here are some common ways to enjoy it:
- Sushi and Sashimi: Often used as a topping for sushi rolls or sashimi, adding a crunchy texture and salty flavor to the dish. Masago.
- Seafood Salads: Mixed into seafood salads for added flavor and texture.Masago.
- Sauces: Stirred into mayonnaise-based sauces or aioli to provide a subtle briny taste. Masago.
- Rice Bowls: Sprinkled over rice bowls for a colorful, flavorful garnish. Masago.
- Tacos or Wraps: A unique topping for tacos or wraps, adding both flavor and a pop of color. Masago.
FAQs
1. Is Capelin Roe the Same as Tobiko?
No, capelin roe and tobiko are different types of fish eggs. Capelin roe comes from the capelin fish, while tobiko is sourced from flying fish. Tobiko is larger, crunchier, and often more expensive than capelin roe. Masago.
2. Can It Be Eaten Raw?
Yes, capelin roe is typically eaten raw, especially when used as a topping for sushi or sashimi. However, it’s important to source it from a reputable supplier to ensure it’s safe to eat. Masago.
3. Is It Safe During Pregnancy?
Pregnant women are often advised to limit their intake of certain seafood due to the risk of mercury and other contaminants. While capelin roe is generally considered low in mercury, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider before consuming it during pregnancy.
4. How Should It Be Stored?
Capelin roe should be stored in the refrigerator and consumed within a few days of opening. For longer storage, it can be frozen and thawed as needed, but it’s best to eat it fresh for optimal flavor and texture. Masago.
Conclusion
In the culinary world, capelin roe is a tiny but mighty ingredient. With its unique texture, mild flavor, and vibrant appearance, it has made its mark, especially in Japanese cuisine. It offers several health benefits, including being high in protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and important vitamins, all while being low in calories. However, it’s not without its downsides, particularly its high sodium content and potential for allergens. Masago.
Incorporating capelin roe into your diet can be a tasty and nutritious choice, but like with anything, moderation is key. Whether you’re enjoying it atop your favorite sushi roll or mixing it into a seafood salad, capelin roe can elevate your culinary experience while contributing to your overall health. Just remember to keep an eye on your sodium intake and always opt for sustainable sources! Masago.
Discover more trends:
- Healthy Breakfast Ideas: The 12 Best Foods to Eat in the Morning
- Ovaltine Healthy? Benefits, Ingredients, and Nutritional Value Explained
- 10 Best Foods to Eat If You Have Arthritis
- Watch Out For The Early Signs Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Follow us on Facebook
- Follow us on Pinterest