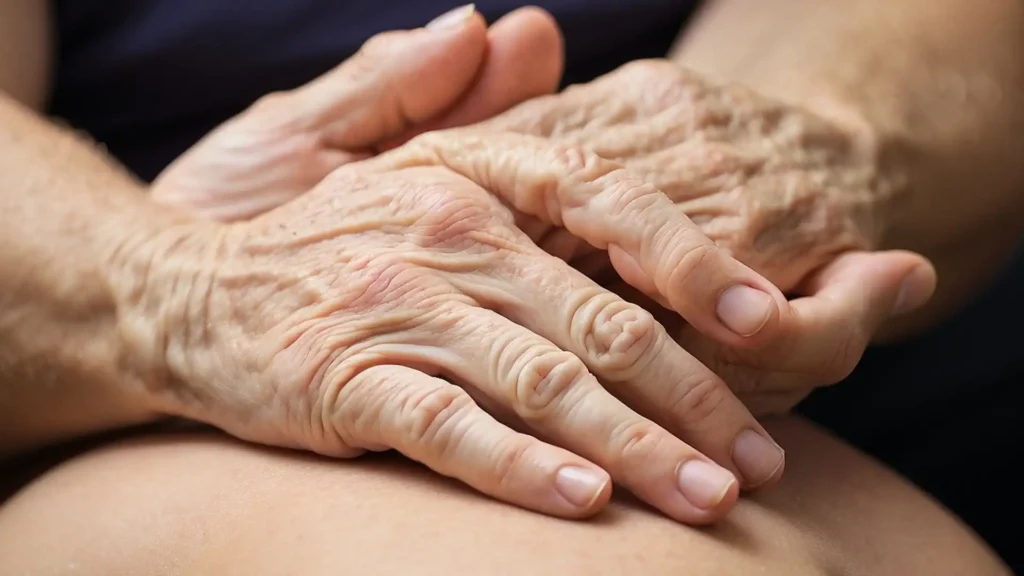
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the joints. In its early stages, the disease may manifest in specific areas such as the hands, often referred to as stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in hands. Timely diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for minimizing the impact of this condition and ensuring a better quality of life.
In this article, we will explore the signs, symptoms, and management strategies for stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis specifically in the hands. We will also discuss the importance of early detection and customized treatment options tailored to individual needs.
Key Takeaways:
- Rheumatoid arthritis can affect various joints in the body, including the hands.
- Early diagnosis of stage 1 rheumatoid arthritis in hands is essential for effective management.
- Physical examinations, imaging tests, and blood work are used to diagnose this condition accurately.
- Managing stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in hands may involve lifestyle adjustments, medication, and physical therapy.
- Customized treatment plans consider individual needs and may include various modalities.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hands
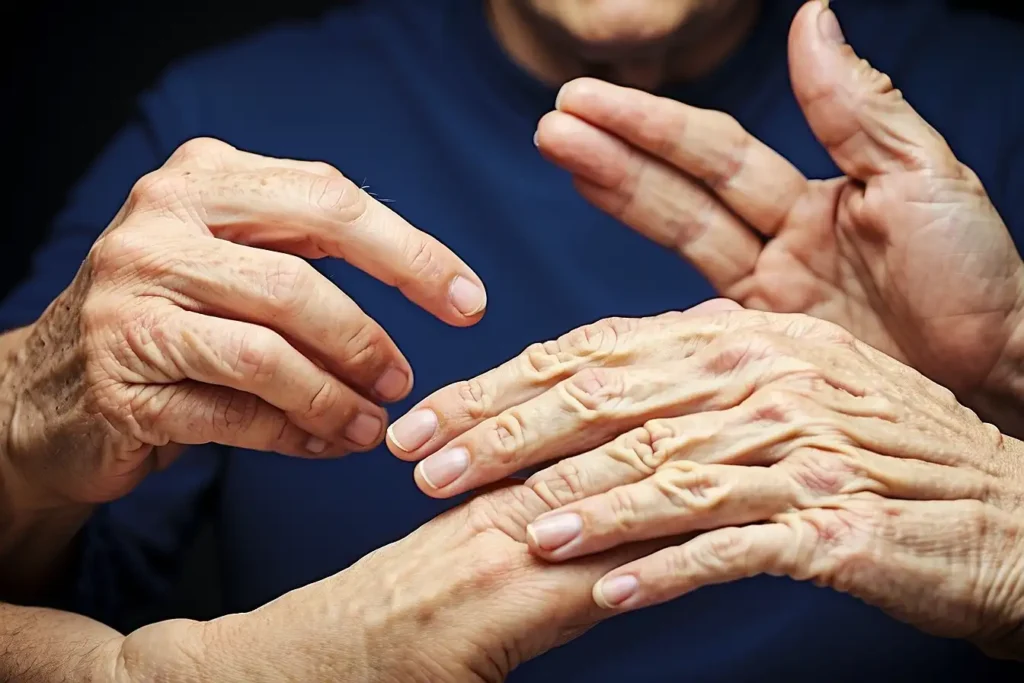
In this section, we will explore the underlying causes and development of rheumatoid arthritis in the hands. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, including those in the hands. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, a membrane that lines the joints.
**Early rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis** is crucial for timely intervention and effective management. Recognizing the **rheumatoid arthritis hand symptoms** can help individuals seek medical attention early on, leading to better outcomes.
Causes and Development
Rheumatoid arthritis in the hands is thought to have a multifactorial origin, including genetic predisposition and environmental factors. The exact cause is still unknown. However, researchers believe that a combination of genetic susceptibility, hormonal factors, and external triggers can contribute to the development of the disease.
Once rheumatoid arthritis develops in the hands, it typically progresses in a symmetrical pattern, affecting both hands simultaneously. The synovium becomes inflamed, causing pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited range of motion in the affected joints.
Early Symptoms in the Hands

Recognizing the early symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in the hands is crucial for **early rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis** and effective management. Some common initial indications may include:
- Persistent joint pain in the hands
- Swelling and tenderness
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity
- Warmth and redness around the affected joints
- Difficulty gripping objects or performing fine motor tasks
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be present in other hand conditions, so seeking a thorough medical evaluation is essential for an accurate diagnosis.
“Early identification of **rheumatoid arthritis hand symptoms** allows for timely intervention, which plays a crucial role in managing the disease effectively.”
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis in the hands involves a comprehensive evaluation, including medical history review, physical examination, imaging tests, and laboratory tests. The healthcare provider may also refer individuals to a rheumatologist, a specialist in diagnosing and treating rheumatic diseases.
In the next section, we will delve into the diagnostic methods used to identify stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands, allowing for accurate and timely intervention.
Diagnosing Stage 1 Early Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hands

When it comes to diagnosing stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in hands, healthcare professionals employ a range of diagnostic methods to accurately identify this condition. These methods help determine the presence of rheumatoid arthritis and assess its severity, enabling healthcare providers to develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
One of the primary diagnostic tools is the physical examination, where healthcare professionals assess the joints in the hands for tenderness, swelling, and limited range of motion. By carefully observing these symptoms and noting any significant changes, they can begin to build a picture of the patient’s condition.
In addition to the physical examination, imaging tests, such as X-rays and ultrasound, are valuable tools in diagnosing stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in hands. X-rays help visualize any joint damage or bone erosion, while ultrasound can identify signs of inflammation in the synovium, a key indicator of rheumatoid arthritis.
Blood work is another essential component of the diagnostic process for rheumatoid arthritis in hands. By analyzing blood samples, healthcare professionals can look for specific antibodies and markers of inflammation, such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies. The presence of these antibodies can aid in confirming a diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis.
Early diagnosis is crucial in managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively. “Detecting and diagnosing the condition in its early stages allows for the implementation of appropriate treatment strategies, which can help prevent further joint damage and limit the progression of the disease,” says Dr. Elizabeth Collins, a renowned rheumatologist.
In some cases, healthcare professionals may also conduct additional tests, such as joint aspiration or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), to gather more information about the condition and rule out other potential causes of hand joint pain and inflammation.
Key Points:
- Physical examination plays a crucial role in detecting early signs of rheumatoid arthritis in hands.
- Imaging tests like X-rays and ultrasound can help visualize joint damage and inflammation.
- Blood work helps identify specific antibodies and markers of inflammation.
- Early diagnosis enables the timely implementation of appropriate treatment strategies.
By utilizing a combination of these diagnostic methods, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in hands, allowing individuals to receive the necessary treatment and support to manage their condition effectively.
Managing Stage 1 Early Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hands
Managing stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands is crucial for maintaining functionality and reducing joint inflammation. There are various strategies and treatments available that can effectively alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with this condition.
1. Lifestyle Modifications
One of the key aspects of managing early rheumatoid arthritis in hands is making lifestyle modifications. This can include implementing joint-protecting techniques, such as using assistive devices and ergonomic tools. Additionally, incorporating regular exercise and maintaining a healthy diet can help control inflammation and enhance overall joint health.
2. Medication

Medication plays a vital role in managing stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids can help reduce pain and inflammation. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may also be prescribed to slow down the progression of the disease and preserve joint function.
3. Physical Therapy

Physical therapy can be highly beneficial for individuals with early rheumatoid arthritis in their hands. A qualified physical therapist can design a customized exercise program that focuses on improving range of motion, strength, and flexibility in the affected joints. They may also employ techniques such as manual therapy and splinting to provide additional support and relief.
4. Assistive Devices
Using assistive devices can greatly assist with managing early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands. Finger splints and braces can provide stability and reduce joint stress, while adaptive tools like jar openers and button hooks can make daily tasks easier. Occupational therapists can assess individual needs and recommend appropriate devices.
It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses the specific needs of individuals with stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in their hands.” – Dr. Sarah Thompson, Rheumatologist
Effective management of early rheumatoid arthritis in hands requires a multi-faceted approach. By implementing lifestyle modifications, utilizing medication as prescribed, engaging in physical therapy, and utilizing assistive devices, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce joint inflammation, manage pain, and maintain optimal hand function.
Customized Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hands
When it comes to managing stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands, customized treatment plans are essential. Each individual’s needs and symptoms are unique, and a tailored approach allows for the most effective management of this condition. Let’s explore the different treatment options available.
1. Medication
Medication plays a crucial role in controlling the inflammation and pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the hands. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents are commonly prescribed. These medications can help reduce joint swelling, stiffness, and deformities, promoting improved hand function.
2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy exercises and techniques are beneficial for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis in the hands. A licensed therapist can design a program focusing on strengthening the hand muscles, improving mobility, and enhancing overall hand function. Additionally, modalities like heat and cold therapy may provide temporary relief from pain and stiffness.
3. Therapy Focused on Work and Daily Activities
Occupational therapy aims to enhance an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks and engage in meaningful activities despite the challenges posed by rheumatoid arthritis in the hands. Occupational therapists can recommend assistive devices, adapt workstations, and provide strategies to conserve energy and protect the joints.
4. Splints and Braces
Splints or braces can be helpful in providing support and stability to the affected joints in the hands. These devices help alleviate pain, reduce swelling, and protect the joints during movement. Custom-made splints are available to ensure a proper fit and maximize the benefits.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
Implementing certain lifestyle modifications can have a significant impact on managing rheumatoid arthritis in the hands. Maintaining a healthy weight, adopting joint-friendly movements and positions, and using assistive devices in daily activities can all help reduce stress on the hand joints and minimize symptoms.
6. Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief from symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in the hands through alternative therapies. Techniques such as acupuncture, massage, and herbal supplements may offer additional relief, although their effectiveness varies from person to person. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any alternative therapies.
Remember, effective treatment for rheumatoid arthritis in the hands often requires a combination of approaches tailored to your individual needs. Working closely with a healthcare team, including rheumatologists, hand therapists, and other specialists, can help you find the most effective treatment plan to manage your condition and improve your quality of life.
Coping with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Hand Pain
Living with early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands can present numerous challenges, particularly when it comes to managing the associated pain. This section offers valuable tips and strategies to help individuals cope with hand pain and improve their overall quality of life.
1. Protecting the Hands
One of the first steps in managing hand pain caused by early rheumatoid arthritis is to protect the hands from further damage. Wearing supportive gloves or braces can help stabilize the joints and reduce strain, especially during activities that involve repetitive hand movements or gripping.
2. Applying Heat or Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapy can provide temporary relief from hand pain. Applying a warm compress or taking a hot shower may help soothe stiff and achy joints. On the other hand, using ice packs or cold compresses can help reduce inflammation and numb the area, providing pain relief.
3. Engaging in Gentle Hand Exercises
Engaging in gentle hand exercises can help improve flexibility, reduce stiffness, and alleviate hand pain. Simple exercises, such as finger stretches, hand squeezes, and thumb rotations, can be performed regularly to keep the joints mobile and reduce discomfort.
4. Using Assistive Devices
Assistive devices can be beneficial in reducing strain on the hands and minimizing pain. Ergonomically designed tools and aids, such as jar openers, button hooks, and adaptive grips, can make daily tasks easier to perform, allowing individuals to continue with their daily activities with less discomfort.
“Coping with hand pain caused by early rheumatoid arthritis requires a multi-faceted approach that focuses on pain management, joint protection, and maintaining overall joint health.” – Dr. Anna Brown, Rheumatologist
5. Seeking Emotional Support
Dealing with hand pain and the challenges associated with early rheumatoid arthritis can take an emotional toll. Seeking support from family, friends, or joining support groups can provide individuals with the opportunity to share their experiences, gain valuable advice, and find emotional reassurance.
6. Exploring Pain Management Techniques
In addition to conventional treatments prescribed by healthcare professionals, individuals with early rheumatoid arthritis can explore various pain management techniques. These may include relaxation techniques, meditation, acupuncture, or physical therapy sessions focused on pain relief.
- Practice deep breathing exercises to promote relaxation and reduce stress levels.
- Explore alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or acupressure, to alleviate hand pain.
- Consider attending physical therapy sessions focused on pain management and strengthening exercises specific to the hands.
- Discuss the use of over-the-counter pain medications with a healthcare professional to determine if they can provide temporary relief.
By implementing these coping strategies and exploring personalized approaches to pain management, individuals with early rheumatoid arthritis in their hands can proactively address their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article has explored the early stage of rheumatoid arthritis specifically in the hands. We have discussed the signs and symptoms that individuals may experience, emphasizing the need for timely diagnosis and intervention. By recognizing the early onset of rheumatoid arthritis in the hands, individuals can work with healthcare professionals to develop personalized treatment plans that effectively manage the condition.
We have also highlighted the importance of accurate diagnosis in stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands. Through physical examinations, imaging tests, and blood work, healthcare professionals can identify the condition and start appropriate treatment promptly. Early diagnosis plays a crucial role in preventing further joint damage and improving long-term outcomes.
Furthermore, we have explored various management strategies and treatment options for stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands. From lifestyle modifications to medication and physical therapy, there are numerous approaches that can help individuals alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and maintain hand function. It is crucial for individuals to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop customized treatment plans for optimal results.
Overall, the key takeaway is that early diagnosis and proper management of stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands are essential in promoting a high quality of life. By recognizing the signs and symptoms, seeking medical attention, and implementing appropriate treatment strategies, individuals can effectively manage this condition and enhance their overall well-being.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands?
Common symptoms of stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands may include joint stiffness, swelling, and pain, particularly in the fingers and wrists. Individuals may also notice difficulty gripping objects or experience a loss of strength in their hands.
How is rheumatoid arthritis in the hands diagnosed at an early stage?
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis in the hands at an early stage typically involves a combination of physical examinations, medical history assessment, imaging tests (such as X-rays or ultrasounds), and blood work to detect specific markers associated with the condition.
What are the treatment options available for managing stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands?
The treatment options for managing stage 1 early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands may include medications (such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), physical therapy exercises, splinting, and lifestyle changes (such as adopting a healthy diet and managing stress).
Can early rheumatoid arthritis in the hands be cured completely?
While there is currently no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment can help manage the symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. With appropriate and consistent management, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite living with this chronic condition.
How can individuals cope with the hand pain associated with early rheumatoid arthritis?
Coping with hand pain in early rheumatoid arthritis can be achieved through various strategies, including using ice or heat packs, practicing gentle exercises to improve flexibility, using assistive devices or adaptive tools to reduce strain on the hands, and seeking the guidance of healthcare professionals for pain management techniques.
Are there any alternative therapies or complementary approaches for managing rheumatoid arthritis in the hands?
Some individuals may find relief from rheumatoid arthritis symptoms in their hands through alternative therapies or complementary approaches, such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and herbal supplements. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any alternative treatment to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Discover more trends:
- Keep an Eye Out for Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Guide
- Nicole Kidman’s Revealing Dress Sparks a Heated Discussion
- Watch Out For The Early Signs Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Follow us on Facebook