Living with rheumatoid arthritis can be challenging, especially when muscle pain becomes a daily struggle. Individuals experiencing rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain understand how it can hinder their daily activities and decrease their quality of life. However, there are various treatment options available to alleviate this discomfort and improve overall well-being. This article will explore different approaches to managing muscle pain in individuals living with rheumatoid arthritis, providing valuable insights and guidance to help find relief. “rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain treatment”
Key Takeaways:
- Rheumatoid arthritis can lead to muscle pain, causing discomfort and hindering daily activities.
- Managing muscle pain effectively is crucial for improving the quality of life of individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain include medication, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and home remedies.
- Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential in developing an individualized treatment plan for managing rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain.
- By combining different treatment approaches and adopting a holistic approach, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis can find relief and enhance their overall well-being.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis and Muscle Pain
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints. However, it can also impact other parts of the body, including the muscles. Individuals with rheumatoid arthritis often experience muscle pain, which can significantly impact their daily lives.
The specific symptoms of muscle pain in rheumatoid arthritis can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience generalized muscle aches and stiffness, while others may have localized pain in specific muscle groups. The severity of muscle pain can also vary, ranging from mild discomfort to debilitating pain that affects mobility.
Several factors contribute to the development of muscle pain in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation plays a crucial role, as the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s tissues, including the muscles, leading to pain and swelling. Over time, this persistent inflammation can cause damage to the muscles, further exacerbating the pain.
Additionally, muscle weakness is common in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, which can further contribute to muscle pain. The inflammation in the joints can lead to reduced activity and immobilization, causing muscles to weaken and atrophy. Weak muscles are more prone to pain and fatigue, making it challenging to perform everyday tasks.
It is important to emphasize that muscle pain in rheumatoid arthritis is not solely a result of the condition’s impact on the joints. The muscles themselves are affected, and addressing muscle pain requires targeted interventions alongside joint-focused treatments.
To effectively manage muscle pain in rheumatoid arthritis, it is crucial to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the underlying inflammation and associated muscle symptoms. This may include a combination of medications, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and home remedies.
By understanding the relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and muscle pain, individuals can work with their healthcare team to create a tailored approach to relieve pain, improve muscle strength, and enhance overall quality of life.
Medications for Rheumatoid Arthritis Muscle Pain

When it comes to managing muscle pain in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, medications play a crucial role in providing relief and improving overall quality of life. There are several types of medications commonly prescribed to address the specific needs of patients.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs are often the first line of defense against rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain. These medications work by reducing inflammation, relieving pain, and improving joint mobility. Common NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin. It is important to note that long-term use of NSAIDs may be associated with gastrointestinal issues, so it’s essential to follow the prescribed dosage and consult with a healthcare professional.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
DMARDs are a class of medications that target the underlying immune system dysfunction responsible for rheumatoid arthritis. They help to slow down disease progression, reduce inflammation, and alleviate muscle pain. Methotrexate and sulfasalazine are examples of commonly prescribed DMARDs for rheumatoid arthritis.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are potent anti-inflammatory medications used for short-term relief of rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain. They provide rapid pain relief and help suppress inflammation. However, long-term use of corticosteroids can lead to side effects, including weight gain, osteoporosis, and increased susceptibility to infections. Therefore, they are usually prescribed at the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible.
Biologic Response Modifiers
Biologic response modifiers, also known as biologics, are advanced medications that target specific proteins or cells involved in the immune response. They help reduce inflammation and slow down joint damage caused by rheumatoid arthritis. Examples of biologics commonly used for muscle pain include adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab. These medications are usually administered via injection or infusion and require close monitoring for potential side effects.
Topical Analgesics
For individuals looking for localized relief from rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain, topical analgesics can be an effective option. These medications are applied directly to the skin over the affected muscles and joints, providing temporary pain relief. Creams, gels, and patches containing ingredients like menthol or capsaicin can help soothe muscle pain and ease discomfort.
Keep in mind that every individual’s condition is unique, and the choice of medication may vary depending on factors such as disease severity, symptoms, and personal preferences. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable medication and dosage for managing rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain.
“Medications for rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain encompass a range of options, from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to biologics. Each medication targets different aspects of the condition and can provide relief for individuals experiencing muscle pain. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to find the most effective treatment approach.”
Physical Therapy and Exercises for Rheumatoid Arthritis Muscle Pain
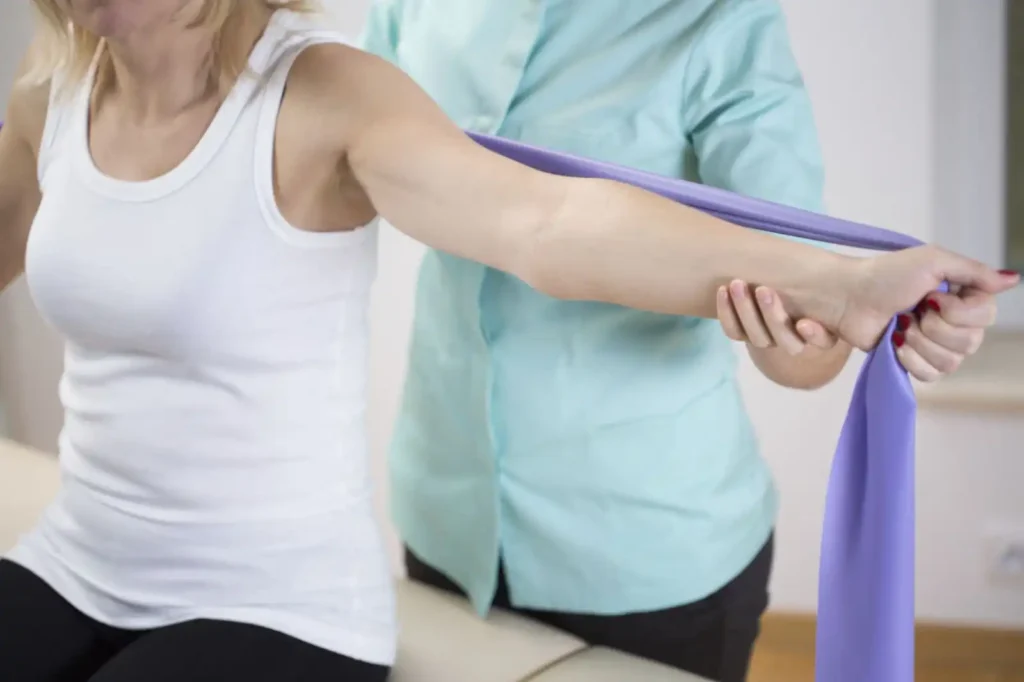

Physical therapy and exercises play a crucial role in managing muscle pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis. By incorporating these therapeutic interventions into a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals can experience improved muscle strength, flexibility, and reduced pain.
One of the key benefits of physical therapy is its ability to target specific muscle groups affected by rheumatoid arthritis. A qualified physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program that focuses on strengthening and stretching the muscles, promoting better joint function and mobility.
Some of the commonly recommended exercises for rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain include:
- Range of motion exercises: These gentle movements help maintain or improve joint flexibility. They can include tasks like stretching, bending, and rotating the affected joints.
- Strengthening exercises: These exercises focus on improving muscle strength around the affected joints, helping to stabilize and support them. They can include activities such as weightlifting, resistance training, and using resistance bands.
- Aerobic exercises: Aerobic exercises, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can enhance cardiovascular health and increase overall endurance. These low-impact activities are gentle on the joints while providing vital benefits for the muscles.
In addition to specific exercises, other physical therapy techniques may be used to manage rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain. These can include heat or cold therapy, ultrasound therapy, and manual therapy, such as massage or joint mobilization.
“Physical therapy and targeted exercises are essential components of rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain management. They help improve muscle strength, flexibility, and overall joint function, leading to reduced pain and enhanced quality of life.” – Dr. Emily Harris, Physical Therapist
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified physical therapist before starting any exercise program for rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain. They can provide individualized guidance and ensure that the exercises are safe and suitable for your specific needs and abilities. Regular communication with healthcare professionals is crucial to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies for Rheumatoid Arthritis Muscle Pain
Managing rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain goes beyond medical treatments alone. Incorporating certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can provide additional support in alleviating pain and improving overall well-being. Here are some tips to consider:
1. Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress can aggravate muscle pain and inflammation in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Implementing stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in activities that promote relaxation, can help reduce stress levels and ease muscle discomfort.
2. Healthy Diet
A well-balanced diet can play a crucial role in managing muscle pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, as they have anti-inflammatory properties. Additionally, consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide essential nutrients to support muscle health.
3. Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity can help strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. Low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, or cycling are gentle on the joints while still providing the benefits of movement. Consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to determine an exercise plan that suits your individual needs and abilities.
4. Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold to affected muscles can provide temporary relief from rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain. Warm compresses or heating pads can help relax tense muscles, while cold packs or ice wrapped in a towel can numb the area, reducing inflammation and discomfort. Always be cautious when using heat or cold therapy to avoid burns or frostbite; use a barrier between the skin and the heat or cold source.
5. Herbal Remedies
Some individuals find relief from rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain through the use of herbal remedies. Turmeric, ginger, and Boswellia are among the herbs that may possess anti-inflammatory properties and help alleviate pain. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating herbal remedies into your treatment plan to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
- Manage stress through meditation, deep breathing, or relaxation techniques.
- Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your diet.
- Engage in regular low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, or cycling to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
- Use heat or cold therapy to temporarily relieve muscle pain.
- Consult with a healthcare professional before using herbal remedies for pain management.
While lifestyle changes and home remedies can provide additional support in managing rheumatoid arthritis muscle pain, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and to ensure these practices align with your specific condition and treatment plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing muscle pain in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis is crucial for improving their overall quality of life. This article has explored various treatment options available, highlighting the importance of finding an individualized approach. It is essential for individuals to consult with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Medications can play a significant role in managing muscle pain, with healthcare professionals prescribing specific drugs based on the severity of the condition. Physical therapy and exercises can also help improve muscle strength and flexibility, reducing pain levels. Additionally, incorporating lifestyle changes and home remedies, such as stress management techniques and a healthy diet, can complement traditional treatments.
It is important to note that every individual’s experience with rheumatoid arthritis and muscle pain is unique. Therefore, personalized advice and support from healthcare professionals are crucial to determine the most effective treatment plan. Through a holistic and comprehensive approach, individuals can reduce muscle pain and enhance their well-being, allowing them to live a more fulfilling life despite their condition.
Discover more trends:
- Keep an Eye Out for Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Guide
- Nicole Kidman’s Revealing Dress Sparks a Heated Discussion
- Watch Out For The Early Signs Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Follow us on Facebook