Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Impact Beyond Joints
“Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is more than just joint pain. Many people experience unusual symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, which can affect multiple organs.”
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is more than just joint pain—it’s a chronic autoimmune disorder that can affect multiple body systems, including the skin, eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels. Unlike osteoarthritis, which results from wear and tear, RA occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s tissues, leading to widespread inflammation and long-term damage.
Table of Contents
Autoimmune Nature of Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA is classified as an autoimmune disease, meaning the body’s defense system turns against itself. This leads to persistent inflammation that not only damages joints but can also impact vital organs and bodily functions. Left untreated, it can result in severe complications, making early diagnosis and management essential.
Joint Impact and Symptoms
RA primarily targets the synovial lining of joints, causing:
- Persistent joint pain and swelling (especially in the wrists, fingers, and knees).
- Stiffness, often worse in the morning or after inactivity.
- Fatigue, due to chronic inflammation and immune system overactivity.
- Low-grade fever and general malaise.
- Loss of appetite and unintended weight loss.
Unusual Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Beyond the well-known joint issues, RA can manifest in unexpected ways, affecting other organs and systems. Some unusual symptoms include: unusual symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Skin issues: Red patches, small lumps (rheumatoid nodules), or ulcers.
- Eye problems: Dryness, pain, redness, and light sensitivity (linked to Sjögren’s syndrome).
- Shortness of breath: Due to lung inflammation or scarring.
- Numbness and tingling: RA can impact nerves, leading to carpal tunnel syndrome or neuropathy.
- Hoarseness or voice changes: Inflammation of the vocal cords can cause persistent voice alterations.
- Heart palpitations or chest pain: RA can increase the risk of pericarditis or heart disease.
Many people with RA remain unaware that these unusual symptoms are linked to their condition, delaying proper treatment. Recognizing these early can lead to better management and improved quality of life.
Progression of Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA often begins in the smaller joints—fingers, toes, and wrists—before advancing to larger joints like knees, elbows, shoulders, and hips. One distinguishing feature is its symmetrical nature, meaning if one side of the body is affected, the other side usually is too.
As RA progresses, joint erosion and deformity become more apparent. In some cases, inflammation spreads to organs like the lungs, heart, and kidneys, further complicating the disease. Roughly 40% of RA patients develop extra-articular symptoms, which go beyond joint pain.
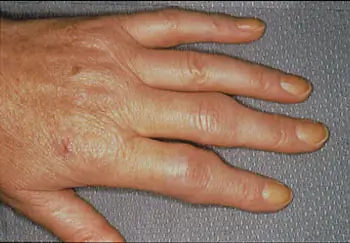
Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Although RA has no cure, effective management can significantly slow its progression and reduce symptoms. Common treatment approaches include:
- Medications: Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, and NSAIDs.
- Lifestyle changes: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and weight management can reduce inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Helps maintain mobility and prevent stiffness.
- Stress management: Since stress can trigger flares, relaxation techniques like yoga and meditation can be beneficial.
RA tends to fluctuate between flares and remission, making personalized treatment plans essential for long-term well-being. unusual symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Early intervention is key to preventing irreversible joint damage and systemic complications. See a doctor if you experience:
- Persistent joint pain and swelling lasting more than six weeks.
- Morning stiffness that lasts over an hour.
- Unusual symptoms like persistent fatigue, shortness of breath, or vision changes.
- Family history of RA, increasing your risk of developing the condition.
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of RA remains unclear, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors likely plays a role. Key risk factors include:unusual symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Gender: Women are up to three times more likely to develop RA.
- Age: RA commonly starts between ages 30 and 50 but can occur at any age.
- Genetics: Having a family history increases susceptibility.
- Smoking: Increases RA risk and worsens symptoms.
- Weight: Higher-weight individuals may have increased inflammation, raising their risk.
While these factors contribute to RA, lifestyle adjustments and early detection can help minimize its impact.
Potential Complications
RA can lead to several serious health complications if left untreated, including:
- Osteoporosis: Increased risk of bone thinning and fractures.
- Rheumatoid nodules: Lumps forming under the skin, usually near joints.
- Severe dry eyes and mouth: Linked to Sjögren’s syndrome.
- Increased infections: Due to a weakened immune system.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: Nerve compression leading to hand numbness.
- Lung disease: Scarring or inflammation affecting breathing.
- Heart disease: RA increases the risk of cardiovascular issues.
- Lymphoma: Some RA patients have a higher risk of developing this blood cancer.
Recognizing these complications early allows for timely intervention and better disease control.unusual symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
Final Thoughts: Taking Control of RA
Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex, systemic condition that extends beyond joint pain. Unusual symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, such as skin issues, nerve problems, and breathing difficulties, often go unnoticed, leading to delayed treatment.
By understanding the early signs, progression, and risk factors, individuals with RA can take proactive steps toward better management, improved mobility, and enhanced quality of life. If you suspect RA, consulting a healthcare provider sooner rather than later can make all the difference.unusual symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
More Information:
Follow us on: 📌 Pinterest | 📘 Facebook