early signs rheumatoid arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints. At its onset, RA can be subtle, making early detection crucial for effective management and improved outcomes. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the early signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, empowering you with the knowledge to recognize and address potential indicators of this condition.
Table of contents
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by inflammation in the lining of the joints, leading to pain, swelling, stiffness, and potential joint deformity. Unlike osteoarthritis, which results from wear and tear on the joints, RA is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissue.
Early Signs and Symptoms
1. Joint Pain and Stiffness
The hallmark symptom of RA is joint pain and stiffness, typically experienced symmetrically on both sides of the body. Morning stiffness lasting for more than an hour is common, with joints feeling tender, warm, and swollen. early signs rheumatoid arthritis
2. Fatigue
Chronic fatigue often accompanies RA, regardless of rest or sleep. This persistent tiredness can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life.
3. Rheumatoid Nodules
These firm lumps form beneath the skin, commonly around pressure points such as elbows, knuckles, or heels. While not present in all cases, rheumatoid nodules can be a distinctive early sign of RA.
4. Joint Redness and Swelling
Inflamed joints may appear red and swollen due to increased blood flow and fluid accumulation. This inflammation contributes to joint tenderness and restricted movement.
5. Fever and Weight Loss
Some individuals with RA may experience low-grade fevers and unintended weight loss, reflecting the systemic nature of the disease and the body’s inflammatory response.
6. Limited Range of Motion
As RA progresses, joint damage can lead to decreased flexibility and limited range of motion. Tasks that once seemed simple, like buttoning a shirt or gripping objects, may become challenging.
When to Seek Medical Advice
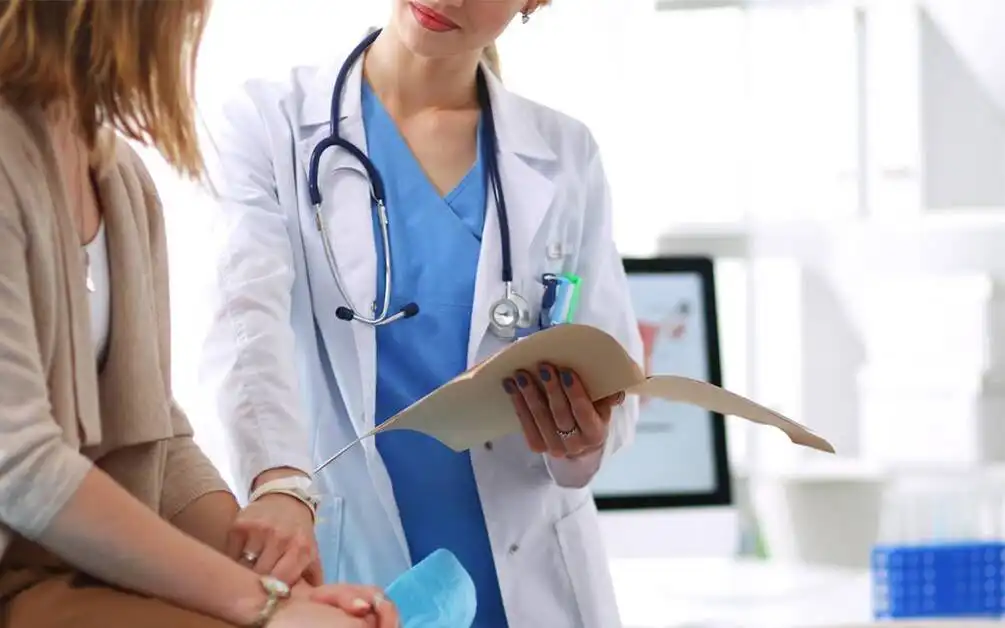

Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively. If you experience persistent joint pain, stiffness, or any of the aforementioned symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional promptly. A rheumatologist, specializing in arthritis and autoimmune disorders, can conduct a thorough evaluation, including physical examination, imaging studies, and blood tests, to confirm a diagnosis of RA.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, various treatment strategies aim to alleviate symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve overall well-being. These may include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents can help reduce inflammation and manage symptoms. early signs rheumatoid arthritis
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, joint protection techniques, and ergonomic adaptations can enhance joint function and mobility. early signs rheumatoid arthritis
- Physical Therapy: Customized exercise programs and therapeutic techniques can improve strength, flexibility, and joint stability. early signs rheumatoid arthritis
- Surgery: In severe cases where joint damage is extensive, surgical interventions such as joint replacement may be necessary to restore function and alleviate pain. early signs rheumatoid arthritis
Conclusion
Early recognition of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis is pivotal in initiating timely treatment and minimizing long-term joint damage. By understanding the early indicators and seeking prompt medical evaluation, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing RA effectively and maintaining a fulfilling quality of life.
Remember, while this article provides valuable insights into rheumatoid arthritis, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized evaluation and management strategies tailored to your individual needs. early signs rheumatoid arthritis
Discover more trends:
Follow us on: 📌Pinterest | 📘 Facebook